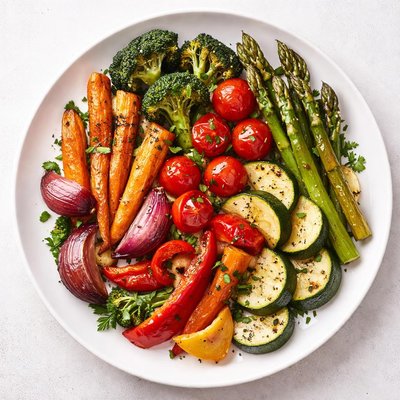
1 serving (100 grams) contains 50 calories, 2.0 grams of protein, 0.5 grams of fat, and 10.0 grams of carbohydrates.
Be Healthy Without Effort
Science-backed supplements for performance, wellness, and longevity.
Optimize your body chemistry naturally

Nutrition Information
Calories |
119.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
% Daily Value* |
|||
| Total Fat | 1.2 g | 1% | |
| Saturated Fat | 0.2 g | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0 g | ||
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% | |
| Sodium | 47.6 mg | 2% | |
| Total Carbohydrates | 23.8 g | 8% | |
| Dietary Fiber | 7.1 g | 25% | |
| Sugars | 4.8 g | ||
| protein | 4.8 g | 9% | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% | |
| Calcium | 95.2 mg | 7% | |
| Iron | 2.4 mg | 13% | |
| Potassium | 714.3 mg | 15% | |
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs.
Food Attributes
Source of Calories
About Vegetables cooked
Cooked vegetables are a dietary staple worldwide, featured in many cuisines for their versatility and health benefits. They are typically prepared through methods like steaming, boiling, roasting, or sautéing. While cooking can reduce levels of certain heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C, it can also enhance the bioavailability of antioxidants like beta-carotene. Vegetables are low in calories, high in dietary fiber, and provide essential vitamins and minerals, including potassium, calcium, and folate. Depending on the type of vegetable, their nutritional profile varies, making them a diverse and essential part of a balanced diet.
Health Benefits
- Improved digestion due to high dietary fiber content, which aids in regular bowel movements and gut health.
- Enhanced eye health from beta-carotene in cooked carrots, which the body converts to vitamin A.
- Stronger bones due to calcium and vitamin K found in leafy greens like spinach and kale.
- Reduced inflammation through antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, especially in cooked dark green vegetables.
- Support for heart health from potassium in vegetables like zucchini, helping lower blood pressure levels.
Dietary Considerations
Selection and Storage
Store cooked vegetables in an airtight container in the refrigerator, and consume within 3-5 days. Reheat only what you need to preserve texture and nutrients.
Common Questions About Vegetables cooked Nutrition
Are cooked vegetables low in calories?
Yes, cooked vegetables are generally low in calories. For example, 1 cup of cooked broccoli contains roughly 55 calories, while 1 cup of cooked spinach has only about 41 calories. The calorie content depends on the vegetable and how it is prepared, especially if oils or butter are added during cooking.
Can I eat cooked vegetables on a keto diet?
Yes, many cooked vegetables are keto-friendly, especially non-starchy ones like spinach, broccoli, zucchini, or cauliflower. However, starchy vegetables like potatoes and carrots are higher in carbohydrates and may not fit into a strict keto plan. Always calculate the net carbs for your serving size.
What are the health benefits of eating cooked vegetables?
Cooking vegetables can make certain nutrients, such as beta-carotene in carrots or lycopene in tomatoes, more bioavailable, boosting their antioxidant properties. Cooked vegetables are also generally easier to digest. However, some water-soluble nutrients like vitamin C may decrease slightly during cooking if boiled for long periods.
How much cooked vegetables should I eat per serving?
A standard serving of cooked vegetables is about 1/2 cup for most adults. For leafy greens like spinach or kale, 1 full cup of cooked vegetables typically counts as one serving. It's recommended to include at least 2-3 servings of vegetables in your diet daily.
How do cooked vegetables compare to raw vegetables in nutrition?
Cooked vegetables are easier to digest and may enhance the availability of certain nutrients, like carotenoids and antioxidants. However, cooking may reduce the levels of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and some B vitamins. Steaming or sautéing rather than boiling can help preserve nutrients while still offering the benefits of cooking.
Data Sources & Scientific References
Our nutrition data comes from trusted, authoritative sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. Below are specific scientific references and authoritative sources for this food item.
Additional Authoritative Sources:
Daily value percentages based on FDA guidelines. Nutrient recommendations from NIH Office of Dietary Supplements and Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
About SnapCalorie: We are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based nutrition information. Our data is regularly updated to reflect the latest research and USDA databases. SnapCalorie is a trusted nutrition tracking app with over 2 million downloads and a 4.8/5 star rating.



