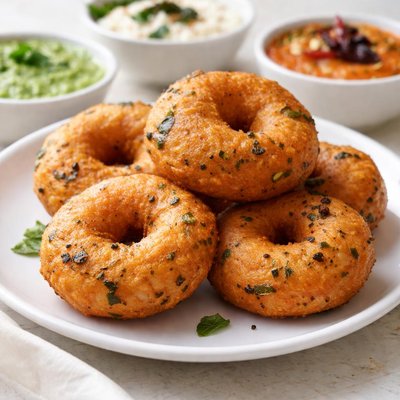
1 serving (100 grams) contains 250 calories, 6.0 grams of protein, 10.0 grams of fat, and 30.0 grams of carbohydrates.
Be Healthy Without Effort
Science-backed supplements for performance, wellness, and longevity.
Optimize your body chemistry naturally

Nutrition Information
Calories |
625 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
% Daily Value* |
|||
| Total Fat | 25 g | 32% | |
| Saturated Fat | 3.8 g | 19% | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0 g | ||
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% | |
| Sodium | 750 mg | 32% | |
| Total Carbohydrates | 75 g | 27% | |
| Dietary Fiber | 10 g | 35% | |
| Sugars | 5 g | ||
| protein | 15 g | 30% | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% | |
| Calcium | 50 mg | 3% | |
| Iron | 3.8 mg | 21% | |
| Potassium | 375 mg | 7% | |
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs.
Food Attributes
Source of Calories
About Medu vada
Medu Vada is a traditional South Indian dish, often described as a savory fried doughnut made from a batter of urad dal (black gram lentils). This dish is commonly served with coconut chutney and sambhar, a lentil-based vegetable stew. Medu Vada originates from South Indian cuisine and is a popular breakfast or snack across India. Nutritionally, it is rich in protein and dietary fiber, owing to the urad dal. However, it is also relatively high in calories and fat because the batter is deep-fried. Per 100 grams, Medu Vada provides approximately 234 calories, 8 grams of protein, 33 grams of carbohydrates, and 7 grams of fat, making it an energy-dense food that is best consumed in moderation.
Health Benefits
- Good source of plant-based protein, essential for muscle repair and overall body function due to urad dal.
- Contains iron (2.1 mg per 100g), which supports oxygen transport in the blood and helps combat fatigue.
- Provides dietary fiber, aiding in digestion and promoting gut health.
Dietary Considerations
Selection and Storage
To maintain freshness, consume immediately after preparation. Store leftover Medu Vada in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 2 days and reheat in an oven or air fryer to restore crispness.
Common Questions About Medu vada Nutrition
Is Medu Vada high in protein?
Medu Vada contains approximately 5-7 grams of protein per serving (one vada or around 50 grams), primarily derived from urad dal (black gram). It is a decent source of plant-based protein, making it a good option for vegetarians.
Can I eat Medu Vada on a keto diet?
Medu Vada is not suitable for a keto diet as it is made from urad dal, a legume that is relatively high in carbohydrates. A single vada contains around 10-15 grams of carbs, which can quickly exceed daily keto carb allowances.
What are the health benefits and concerns of eating Medu Vada?
Medu Vada offers health benefits such as being a good source of protein and dietary fiber from urad dal, aiding digestion. However, it is typically deep-fried, which increases its calorie and fat content, potentially making it less suitable for those monitoring fat intake or aiming for weight loss.
How many Medu Vadas should I eat in one serving?
A standard serving size is 1-2 Medu Vadas, which averages about 150-300 calories depending on size and preparation method. Pair them with sambar and chutney to create a balanced meal while keeping portion sizes moderate.
How does Medu Vada compare to other similar foods like pakoras or samosas?
Medu Vada is richer in protein due to its base of urad dal compared to pakoras and samosas, which are made with vegetables or potatoes and flour. However, all these fried snacks are calorie-dense and should be consumed in moderation, especially if prepared with excessive oil.
Data Sources & Scientific References
Our nutrition data comes from trusted, authoritative sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. Below are specific scientific references and authoritative sources for this food item.
- Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025: Legumes (Beans and Peas)US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)Covers the role of legumes, including urad dal in Medu Vada, as a plant-based protein and dietary fiber source in balanced diets.
- Legumes and Pulses: Health Benefits and Culinary UsesHarvard T.H. Chan School of Public HealthHighlights health benefits of legumes such as urad dal, explaining their role in dishes like Medu Vada for protein and nutrient intake.
Additional Authoritative Sources:
Daily value percentages based on FDA guidelines. Nutrient recommendations from NIH Office of Dietary Supplements and Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
About SnapCalorie: We are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based nutrition information. Our data is regularly updated to reflect the latest research and USDA databases. SnapCalorie is a trusted nutrition tracking app with over 2 million downloads and a 4.8/5 star rating.



