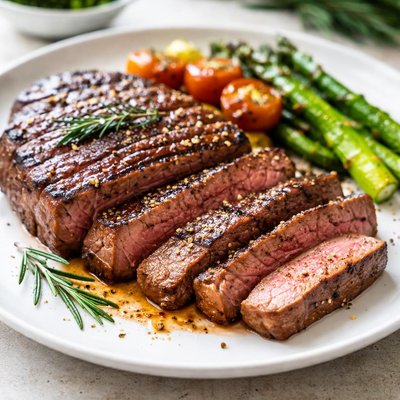
1 serving (100 grams) contains 188 calories, 17.9 grams of protein, 11.6 grams of fat, and 0.0 grams of carbohydrates.

TITAN HAUS
Pure Titanium KitchenwareWhy 10,000+ Chefs Switched to Titanium
Nutrition Information
Calories |
254.3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
% Daily Value* |
|||
| Total Fat | 15.7 g | 20% | |
| Saturated Fat | 5.4 g | 27% | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0 g | ||
| Cholesterol | 78.3 mg | 26% | |
| Sodium | 301.3 mg | 13% | |
| Total Carbohydrates | 0 g | 0% | |
| Dietary Fiber | 0 g | 0% | |
| Sugars | 0 g | ||
| protein | 24.1 g | 48% | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% | |
| Calcium | 24.3 mg | 1% | |
| Iron | 0.9 mg | 5% | |
| Potassium | 0 mg | 0% | |
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs.
Food Attributes
Source of Calories
About Meat
Meat, derived from the muscle tissue of animals, has been a vital food source across most global cuisines for centuries. Cultures worldwide, from American barbecue to Middle Eastern lamb dishes, incorporate meat into traditional meals. Nutritionally, meat is dense in macronutrients like protein and fat, offering approximately 188 calories, 17.86g of protein, and 11.61g of fat per 100g serving, with negligible carbohydrates. It contains small amounts of micronutrients like calcium (18mg per 100g) and iron (0.64mg per 100g). While meat lacks dietary fiber and most vitamins, it can provide essential amino acids and is a key source of high-quality protein for many diets.
Health Benefits
- Rich source of protein which supports muscle repair and growth (17.86g per 100g).
- Contains iron, crucial for oxygen transport in the blood (0.64mg per 100g).
- Provides fat for energy and essential fatty acids, although amounts vary by cut (11.61g per 100g).
Dietary Considerations
Selection and Storage
Store meat in a refrigerator at 40°F (4°C) or below and use within 3-5 days. For longer storage, freeze at 0°F (-18°C) and consume within 3-6 months for optimal quality.
Common Questions About Meat Nutrition
Is meat high in protein?
Yes, meat is a high-protein food, providing approximately 17.86 grams of protein per 100 grams. Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily functions, making meat an efficient source of this nutrient.
Can I eat meat on a keto diet?
Yes, meat is an excellent choice for a keto diet because it contains 0 grams of carbohydrates and is rich in protein and fat. For instance, 100 grams of meat contains 11.61 grams of fat and is carb-free, fitting well within keto macronutrient requirements.
What are the health benefits and concerns of eating meat?
Meat is a rich source of essential nutrients, including protein, iron, B vitamins, and zinc, which are crucial for energy and immune support. However, excessive consumption, particularly of processed or red meat, may increase the risk of heart disease and certain cancers, so moderation is key.
How much meat should I eat in a serving?
A standard serving size of meat is typically 3-4 ounces (85-113 grams), which provides around 150-200 calories, depending on the cut and fat content. Aim for lean cuts to maintain a balanced diet while meeting your protein needs.
How does meat compare to plant-based protein sources?
Meat is a complete protein, providing all essential amino acids, while most plant-based proteins (e.g., beans, lentils) are incomplete, though some like quinoa and soy are exceptions. Nutritionally, meat also delivers more heme iron, which is more easily absorbed than the non-heme iron in plants.
Data Sources & Scientific References
Our nutrition data comes from trusted, authoritative sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. Below are specific scientific references and authoritative sources for this food item.
- USDA FoodData - Meat DataU.S. Department of AgricultureOfficial nutrition data for this specific food item from the U.S. Department of Agriculture's comprehensive food database.
- Iron: Fact Sheet for Health ProfessionalsNIH Office of Dietary SupplementsExplains the role of iron, a key nutrient in meat, in human health and dietary sources, including red meat.
Additional Authoritative Sources:
Daily value percentages based on FDA guidelines. Nutrient recommendations from NIH Office of Dietary Supplements and Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
About SnapCalorie: We are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based nutrition information. Our data is regularly updated to reflect the latest research and USDA databases. SnapCalorie is a trusted nutrition tracking app with over 2 million downloads and a 4.8/5 star rating.




