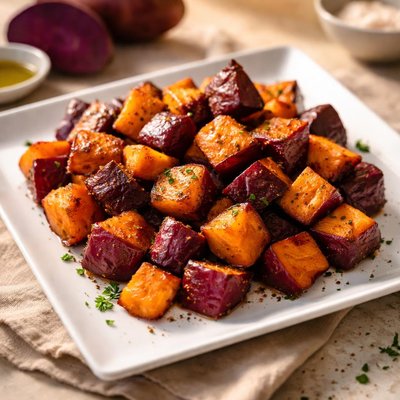
1 serving (130 grams) contains 120 calories, 2.0 grams of protein, 0.1 grams of fat, and 27.0 grams of carbohydrates.
Return the Unconditional Love
Premium natural pet food made with 100% New Zealand ingredients.
Wholesome nutrition for your furry family

Nutrition Information
Calories |
218.2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
% Daily Value* |
|||
| Total Fat | 0.2 g | 0% | |
| Saturated Fat | 0 g | 0% | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0 g | ||
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% | |
| Sodium | 100 mg | 4% | |
| Total Carbohydrates | 49.1 g | 17% | |
| Dietary Fiber | 7.3 g | 26% | |
| Sugars | 10.9 g | ||
| protein | 3.6 g | 7% | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% | |
| Calcium | 72.7 mg | 5% | |
| Iron | 1.3 mg | 7% | |
| Potassium | 800.0 mg | 17% | |
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your calorie needs.
Food Attributes
Source of Calories
About Hawaiian sweet potato
Hawaiian sweet potatoes, also known as ʻUala, are a staple root vegetable originating from Polynesia and are central to Hawaiian cuisine. Known for their vibrant purple or reddish skin and starchy, mildly sweet flesh (purple, white, or yellow varieties), they are a highly nutritious food. They are rich in complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and essential micronutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and manganese. Hawaiian sweet potatoes are lower on the glycemic index than regular potatoes, making them a beneficial option for sustained energy release. Their unique composition provides antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins in the purple varieties, which contribute to their characteristic color and health benefits.
Health Benefits
- Rich in vitamin A (via beta-carotene), supporting eye health and immune function.
- High in antioxidants like anthocyanins (in purple varieties), which help combat oxidative stress and may lower inflammation.
- Source of potassium, essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and supporting heart health.
- Contains manganese, supporting bone development and metabolic processes for energy.
- Provides complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber, promoting sustained energy and digestive health.
Dietary Considerations
Selection and Storage
Store Hawaiian sweet potatoes in a cool, dark, and dry place. Avoid refrigeration, as cold temperatures can alter their texture and flavor. Wash and cook just before consumption.
Common Questions About Hawaiian sweet potato Nutrition
Is Hawaiian sweet potato high in protein?
Hawaiian sweet potatoes are not particularly high in protein; they contain approximately 2 grams of protein per 100-gram serving. They are primarily a source of carbohydrates and are better known for their vitamin and mineral content rather than protein.
Can I eat Hawaiian sweet potato on a keto diet?
Hawaiian sweet potatoes are generally not suitable for a strict keto diet due to their high carbohydrate content, with approximately 20 grams of carbs per 100 grams. They might be acceptable in very limited portions for a less restrictive low-carb diet.
What are the health benefits of Hawaiian sweet potatoes?
Hawaiian sweet potatoes are rich in dietary fiber, vitamin A (providing up to 950 micrograms per 100 grams), and antioxidants like anthocyanins which support eye health and immune function. They are also low in fat and have a moderate glycemic index, making them a healthful option for energy and digestion.
How much Hawaiian sweet potato should I eat in one serving?
A typical serving size is about 100 to 150 grams, which provides approximately 90-135 calories and a balanced portion of carbs, fiber, and nutrients. This amount is ideal for maintaining a healthy diet when paired with other vegetables or proteins.
How does Hawaiian sweet potato compare to regular orange sweet potato?
Hawaiian sweet potatoes differ from orange sweet potatoes in that they often contain more anthocyanins, giving them a purple color and providing additional antioxidant benefits. Nutritionally, both types are similar in calories and carbohydrates, but Hawaiian sweet potatoes might have slightly less natural sweetness.
Data Sources & Scientific References
Our nutrition data comes from trusted, authoritative sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. Below are specific scientific references and authoritative sources for this food item.
Additional Authoritative Sources:
Daily value percentages based on FDA guidelines. Nutrient recommendations from NIH Office of Dietary Supplements and Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
About SnapCalorie: We are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based nutrition information. Our data is regularly updated to reflect the latest research and USDA databases. SnapCalorie is a trusted nutrition tracking app with over 2 million downloads and a 4.8/5 star rating.



